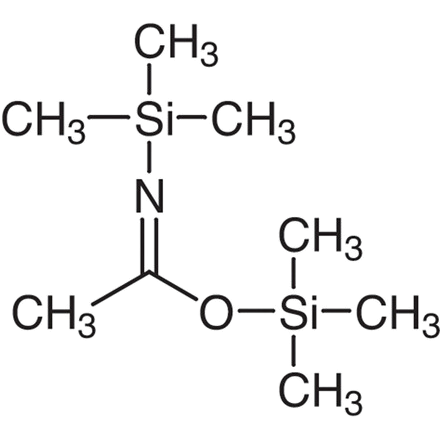
N,O-BIS (TRIMETHYLSILYL) ACETAMIDE
YAC-BSA N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide (BSA) is a highly effective silylating agent commonly used for the protection of various functional groups such as amides, amines, alcohols, carboxylic acids, enols, and phenols. It functions by introducing trimethylsilyl (TMS) groups onto these functional groups, thereby providing protection from unwanted chemical reactions or transformations.
BSA is particularly valuable in organic synthesis and chemical reactions where the preservation of specific functional groups is crucial. It offers enhanced stability and compatibility with a wide range of organic compounds, making it a versatile reagent in many synthetic methodologies. By selectively silylating target functional groups, BSA helps to shield them from undesired reactions, allowing for controlled transformations elsewhere in the molecule.
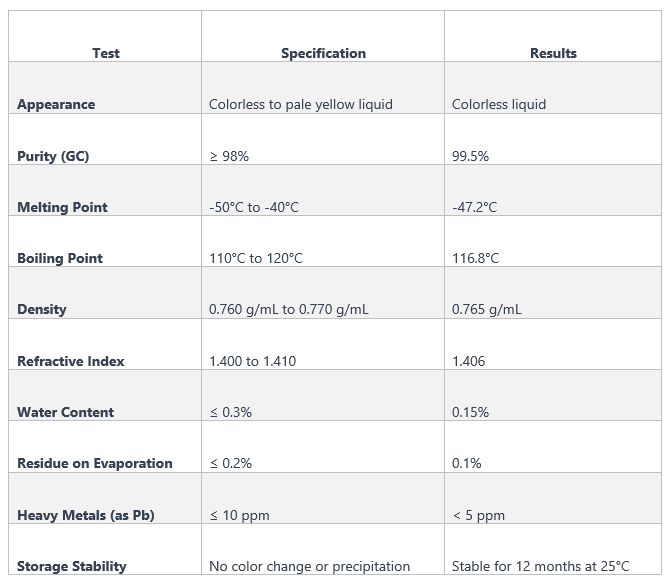
Specification
Advanced
Product Information
Protection of Amides: BSA is commonly used to protect amides by introducing trimethylsilyl (TMS) groups onto the nitrogen atom. This protection prevents unwanted reactions and allows selective modification of other functional groups within the molecule.
Protection of Amines: BSA can selectively protect primary and secondary amines by silylating the nitrogen atom. This protection is valuable in multi-step synthesis, where it enables control over specific amine reactions while keeping other functional groups intact.
Protection of Alcohols: BSA is employed for the protection of alcohols by introducing TMS groups onto the hydroxyl group. This protection is particularly useful in reactions where alcohols may be sensitive to certain reagents or conditions, allowing for controlled transformations without affecting the alcohol functionality.
Protection of Carboxylic Acids: BSA can protect carboxylic acids by introducing TMS groups onto the carboxyl group. This protection is beneficial in reactions that involve acidic conditions or reactive reagents, providing stability to the carboxylic acid functionality.
Protection of Enols: BSA is used to protect enols, which are important intermediates in various synthetic transformations. The introduction of TMS groups onto the enol functionality prevents unwanted reactions, allowing for selective modifications in other parts of the molecule.
Protection of Phenols: BSA can protect phenols by introducing TMS groups onto the hydroxyl group. This protection is valuable in reactions where phenols may undergo undesired reactions, ensuring their preservation and enabling controlled modifications elsewhere in the molecule.





