Trimethylchlorosilane
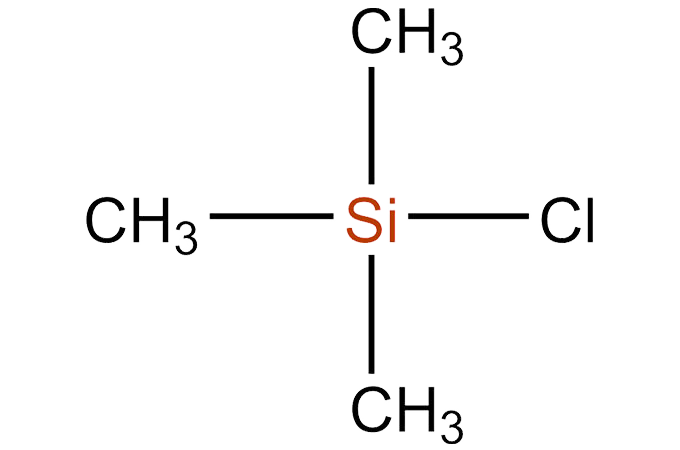
Trimethylchlorosilane is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCl. It is commonly referred to as TMCS. TMCS belongs to the class of organosilicon compounds known as organochlorosilanes.
Trimethylchlorosilane is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It is highly reactive and can react violently with water, releasing hydrogen chloride gas. Due to its reactivity, it is typically stored and handled under anhydrous conditions. TMCS is widely used in organic synthesis and as a reagent in various chemical reactions. It is commonly employed as a silylating agent, which means it can introduce trimethylsilyl (-Si(CH3)3) groups into organic molecules. This silylation process is useful for protecting sensitive functional groups or enhancing the volatility and stability of compounds.
In addition to its role in organic synthesis, trimethylchlorosilane finds applications in the semiconductor industry. It is used as a precursor in the production of silicon-based materials and coatings. TMCS can be used to deposit thin films of silicon dioxide or silicon nitride on surfaces, which are important for the fabrication of microelectronics and integrated circuits.
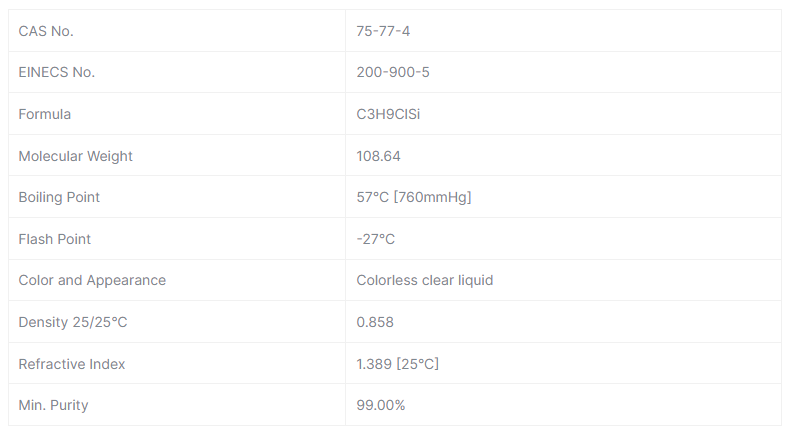
Specification
Advanced
Product Information
All chlorosilanes react with water to produce hydrogen chloride. The remaining hydroxyl group bonds to the silicon, initially forming a silol group (analogous to alcohol). In general, this will eventually bond to a solid oxide surface or react with another chlorosilane or silol molecule. In the latter cases, the oxygen atom forms a link between two silicon atoms, analogous to the ether linkage in organic chemicals, and identical to the bonding in silicon dioxide.
Methyl chlorosilanes have one to three methyl groups. In the case of dichlorodimethylsilane, two chlorine atoms are available, so that a reaction with excess water produces a linear chain of ether-like linkages between silicon atoms. As in polyethers, these flexible linkages produce a rubbery polymer, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Trichloromethylsilane can be used to induce branching and cross-linking in PDMS molecules, while chlorotrimethylsilane serves to end backbone chains, limiting molecular weight.
Organic chlorosilanes are usually used as coatings for silicon and glass surfaces, and in the production of silicone polymers.
YAC-TMCS trimethylchlorosilane cas no. 75-77-4 is a typical Silane Blocking Agent, which can protect or deprotect functional groups selectively. It is widely used in the syntheses of drugs.
YAC-TMCS organofunctional silanes are supplied in net weight 170Kg steel drum.
In the unopened original container YAC-TMCS trimethylchlorosilane has a shelf life of one year in a dry and cool place.





